Pickering’s Triangle: Unveiling the Beauty of Stellar Remnants
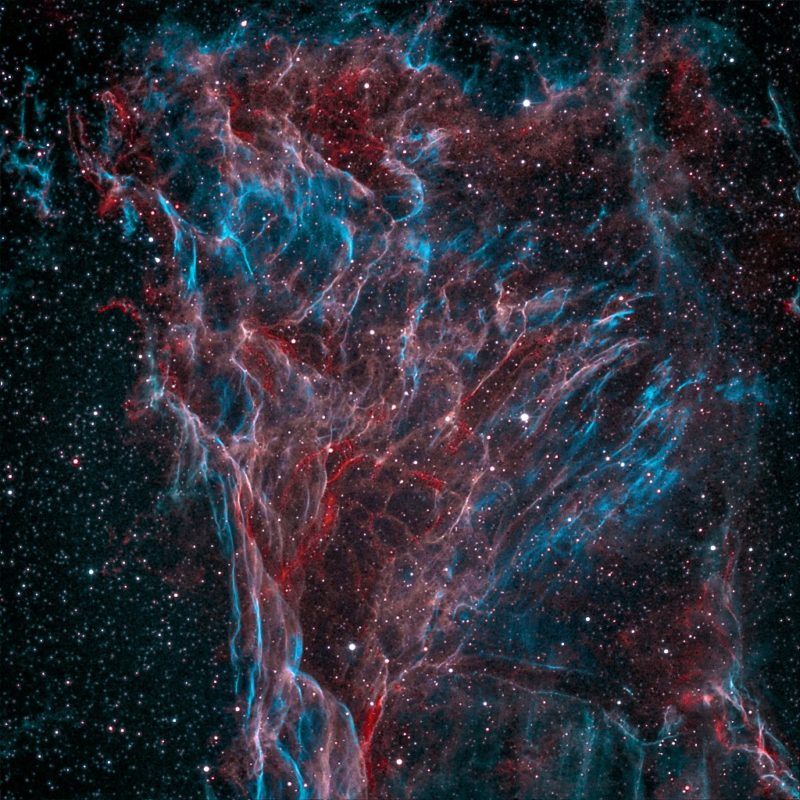

In the constellation Cygnus, a celestial masterpiece unfolds—the Veil Nebula. Within its intricate folds lies Pickering’s Triangle, a luminous mystery born from the explosive demise of a massive star. Let’s delve into this captivating cosmic tapestry, exploring its unique features and the intriguing story behind its discovery and name.
Location
Nestled within the sprawling expanse of the constellation Cygnus, Pickering’s Triangle resides as a radiant jewel within the Veil Nebula. This celestial tapestry spans across a significant portion of the northern sky, offering astronomers a breathtaking view of cosmic remnants from a stellar explosion that occurred thousands of years ago.
The Veil Nebula or Cygnus Loop, comprising several distinct sections, is a supernova remnant—a dazzling aftermath of a massive star’s dramatic demise. Among its intricate filaments and clouds of ionized gas lies Pickering’s Triangle, an area that stands out for its brightness and distinct features. The Veil Nebula also includes the Eastern Veil Nebula as well as the Witch’s Broom Nebula.
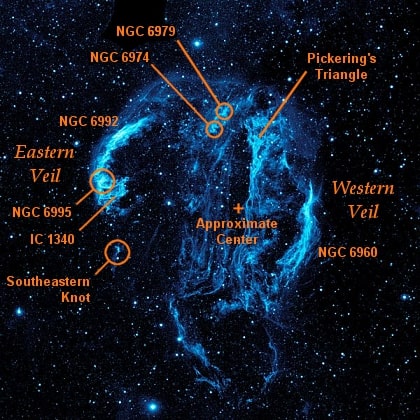
Located approximately 2400 light-years away from Earth, Pickering’s Triangle captivates observers with its intricate details and serves as a testament to the immense forces unleashed during a supernova event. Its positioning within the larger Veil Nebula provides astronomers with a unique vantage point to study the aftermath of stellar explosions and unravel the secrets hidden within these cosmic remnants.
The region’s location in the constellation Cygnus, a prominent and easily identifiable constellation in the northern hemisphere, allows for accessible observation and scrutiny, making it an intriguing target for both amateur and professional astronomers seeking to explore the wonders of the universe.
Notable Features and Characteristics
Pickering’s Triangle stands out amidst the Veil Nebula due to its distinctive luminosity and intriguing structural elements. This section of the nebula showcases a vibrant display of ionized gases—glowing clouds of hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur—painting a mesmerizing portrait of cosmic remnants.
Filamentary Structure
One of the most striking aspects of Pickering’s Triangle is its intricate filamentary structure. The remnants display a delicate, web-like pattern, weaving through the cosmic landscape. These filaments, composed of gas and dust, bear witness to the shockwaves from the supernova explosion that propagated through the interstellar medium.
Expansion and Evolution
Pickering’s Triangle continues to expand and evolve over millennia. Observations and measurements of its expansion rate provide crucial insights into the dynamics of the supernova explosion and the subsequent interactions with the interstellar medium. Tracking this expansion offers astronomers a unique opportunity to understand the processes governing the evolution of supernova remnants.
Multi-Wavelength Observations
Studying Pickering’s Triangle across various wavelengths, from radio to X-ray, reveals different facets of its composition and physical properties. Observations conducted using different instruments and techniques allow astronomers to construct a comprehensive understanding of the nebula’s structure and the underlying mechanisms at play.
Discovery and Naming
Pickering’s Triangle, was actually discovered by Scottish-American astronomer Williamina Fleming, but credit went to Edward Charles Pickering who was the director of her observatory (Harvard College Observatory), as was the custom at the time. Despite this, sometimes the object is refereed to as Fleming’s Triangle instead, albeit rarely.
It was discovered in 1904, after the New General Catalogue was already published, which explains why such a large and prominent object does not have an NGC designation. An alternate name for the object is Pickering’s Triangular Wisp.
Conclusion
Pickering’s Triangle, nestled within the Veil Nebula in Cygnus, is a cosmic marvel revealing the aftermath of a supernova. Its luminous filaments and gases stand testament to a stellar explosion’s enduring beauty and complexity.
In its intricate details, Pickering’s Triangle embodies the cosmic drama and the awe-inspiring forces that shape our celestial landscape, a testament to the enduring quest to understand the vast expanse of our cosmos.
Would you like to receive similar articles by email?