Pelican Nebula Unveiled: A Stellar Odyssey through Cygnus

Nestled in the vastness of the Cygnus constellation, the Pelican Nebula beckons with its alluring mysteries. This celestial masterpiece, shaped like a cosmic pelican, teases us with ethereal wonders and newborn stars.
Join us as we journey through its cosmic dance—exploring its unique location and unraveling its captivating features. Brace yourself for a cosmic adventure, where the Pelican Nebula unfolds its celestial secrets in the heart of the Milky Way.
Pelican Nebula Location
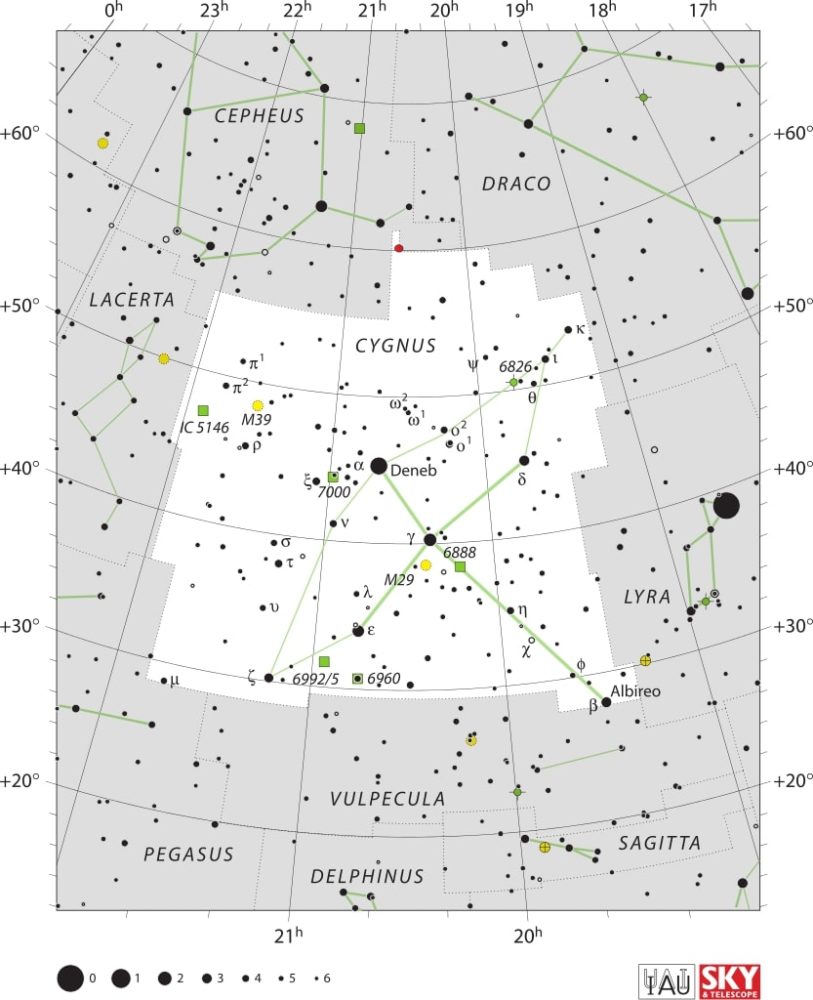
The Pelican Nebula, also known as IC 5070 and IC 5067, is located in the Cygnus constellation approximately 2,590 light years away. Its celestial coordinates place it in close proximity to two other notable objects: the North America Nebula (NGC 7000) and the first magnitude star Deneb. Both nebulae are part of the larger H II region of Westerhout 40, also designated as Sh2-117 in the Sharpless catalog.
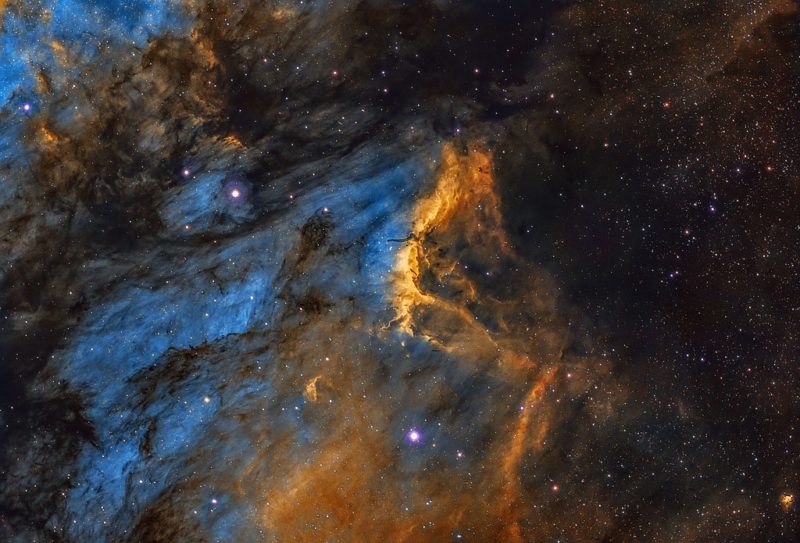
Notable Features and Characteristics
As we turn our gaze towards the Pelican Nebula’s captivating features, a cosmic tapestry unfolds. Shaped like a celestial pelican in flight, this nebulous wonder unveils a spectacle that transcends the ordinary. Within its bounds, ionized hydrogen gas, intricately interwoven with cosmic dust, forms a canvas upon which the radiance of young, hot stars paints a mesmerizing picture.
Distinctive Pelican-like Shape
The Pelican Nebula’s most recognizable feature is its distinct pelican-like shape, a celestial formation that captures the imagination of astronomers and stargazers alike. The nebula’s structure, resembling a cosmic bird in flight, adds a unique aesthetic quality to this stellar entity, setting it apart within the vast canvas of the Cygnus constellation.
Ionized Hydrogen Gas
This emission nebula and H II region is a rich reservoir of ionized hydrogen gas which forms the luminous and colorful nebulous structures that characterize this celestial marvel. The ionization process, often induced by the intense radiation from nearby stars, contributes to the nebula’s vibrant appearance and provides a visual feast for those observing this region of the cosmos.
Cosmic Dust Clouds
Interwoven with the ionized hydrogen gas are cosmic dust clouds, adding depth and complexity to the Pelican Nebula’s visual tapestry. These dusty regions, often illuminated by the surrounding stars, create contrasting dark and light areas, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal and revealing the intricate interplay between matter and radiation.
Stellar Winds and Radiation
Dynamic forces within the Pelican Nebula, such as stellar winds and intense radiation from young, hot stars, sculpt the surrounding interstellar material. These powerful cosmic influences contribute to the formation of intricate structures, shaping the nebula’s appearance and adding a dynamic dimension to its cosmic landscape.
Intricate Network of Structures
Exploring the Pelican Nebula reveals a complex network of interstellar structures. These formations, sculpted by the forces at play within the nebula, showcase the intricate beauty of cosmic architecture. The interplay of these structures adds layers of complexity to our understanding of the nebula’s formation and evolution.
Ongoing Star Formation
Embedded within the Pelican Nebula are stellar nurseries, where new stars are born from the surrounding gas and dust. This ongoing star formation process contributes to the rejuvenation of the nebula, perpetuating the cycle of stellar life within this cosmic environment.
Herbig-Haro Object 555
Nestled within the intricate structures of the Pelican Nebula is the fascinating Herbig-Haro object 555. This astronomical phenomenon, marked by narrow, jet-like streams of gas ejected from a young star, adds an intriguing layer to the nebula’s cosmic narrative. Herbig–Haro objects, including HH 555, provide astronomers with a glimpse into the early stages of star formation, contributing to our comprehension of the dynamic processes shaping the Pelican Nebula and the celestial events occurring within its bounds.
Conclusion
In short, the Pelican Nebula stands as a captivating cosmic marvel, unveiling the intricacies of ionized hydrogen, cosmic dust, and the celestial ballet of newborn stars. Explored alongside the Herbig-Haro object 555, it provides insights into early star formation. Nestled in the Milky Way, the nebula echoes the wonders of the night sky and enriches our understanding of the universe’s perpetual dynamism. This cosmic pelican leaves us with a deep appreciation for the beauty woven into the fabric of our celestial tapestry.
Would you like to receive similar articles by email?