How Did Jupiter Get Its Name?
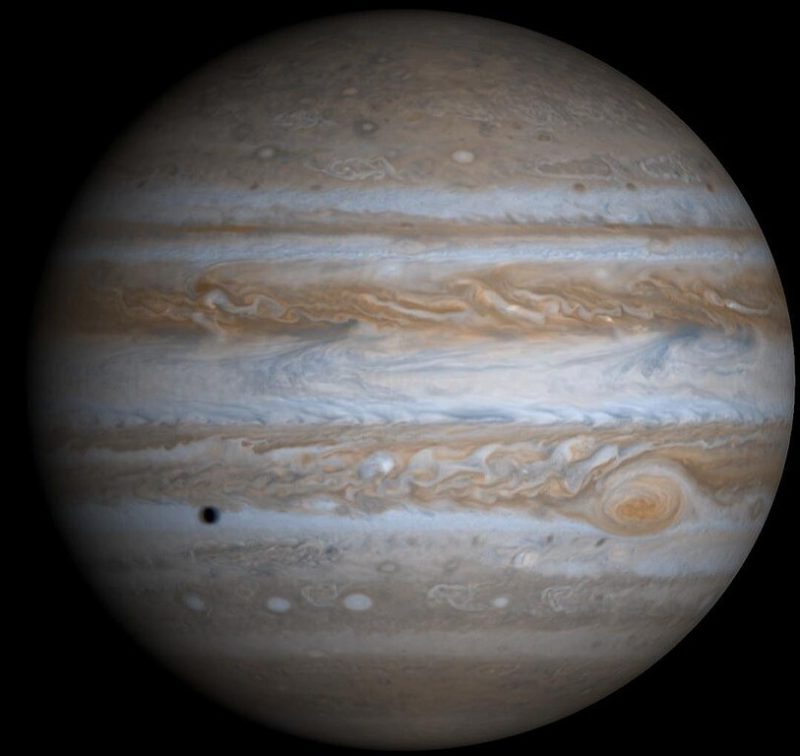

Jupiter, the king of the gods and largest planet of our solar system, has a name that is deeply entrenched in ancient mythology. Named after the Roman king of the gods, Jupiter embodies all the majesty and power that its namesake would expect. This tradition of naming goes all the way back to Roman times.
In ancient times, people credited the planets they could see with attributes of their gods. The selection of Jupiter for this biggest of the planets underscores its preeminence and kingly aspect in the heavens.
The story behind Jupiter’s name is a unique blend of history, mythology, and astronomy. Understanding the connection between art and science better informs our view of the world around us.
Origin of Jupiter’s Name
One of the most recognizable names in our solar system, Jupiter — the largest planet by far — has a name that dates back to ancient Rome. Named after the king of the Roman gods, Jupiter had long been considered the most important object in the Roman night sky. This selection reflects the planet’s great size and luminosity.
Perhaps more importantly, it underscores Jupiter’s robust supremacy in the night sky. Even the planet’s moons, such as Ganymede and Callisto, are named and linked profoundly to Jupiter’s mythological legacy. Their being named after figures with mythological connections to Jupiter deepens the planet’s celestial identity.
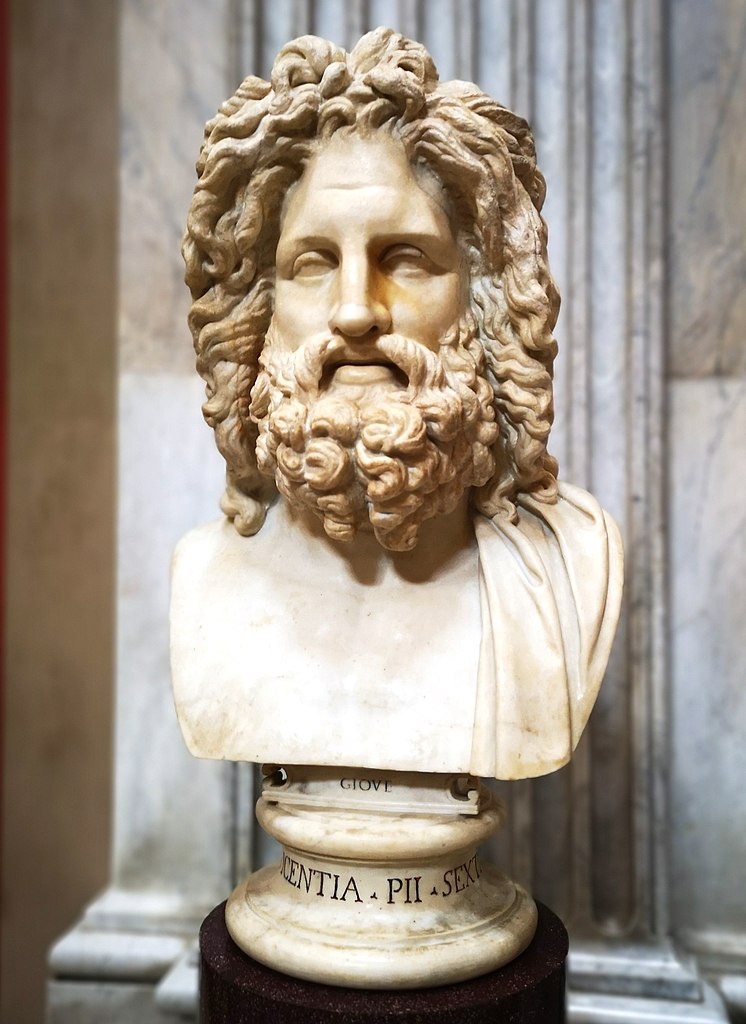

Etymology of Jupiter’s Name
The name “Jupiter” traces its etymology back through Latin “Iuppiter,” showing its lineage in ancient languages. This name links back to the chief god idea, representing authority and heavenly power.
Ensuing changes in language have altered the pronunciation and spelling, but the connection between the name and divine leadership has been kept. The Romans did see Jupiter as the supreme god of sky and thunder.
Linguistically, Jupiter’s name mirrors its characteristics: vastness, dominance, and a mysterious atmosphere, mostly hydrogen, with a core hotter than 19,700 °C.
Mythological and Cultural Significance
Mythological Associations
Jupiter has a special place in Roman mythology, just like his Greek counterpart, Zeus. Both are worshiped as the chief gods of gods, and are connected with thunder and lightning. These elements represent their incredible power and dominion over nature and divine miracles.
In fact, Jupiter’s tales are interlaced between many cultures, frequently wrapping around tales of other gods, such as Marduk in Babylonian mythology. These intersections speak to common themes of authority, leadership, and consequence.
Jupiter rules as the god of sky and thunder, exerting great influence over a multitude of mythological stories. His impact deepens the association with celestial events, influencing how ancient cultures perceived the universe around them.
Symbolism in Roman Culture
Jupiter’s influence goes further than just Roman mythology, reaching across into culture. Usually regarded as an emblem of growth and wealth, Jupiter’s qualities ascribed to him have overflown into works of art and literature.
In Roman culture, Jupiter was represented by important symbols such as the eagle and the thunderbolt. These dynamic motifs circulated through the empire on coins and public monuments.
Influence on Literature and Art
In Roman times, poets such as Virgil and Ovid reanimate Jupiter’s character. As the hero of the people, he embodies powerful themes of divine intervention and moral authority.
Artists throughout history have captured Jupiter’s majesty in paintings and sculptures, depicting him amidst thunderclouds or wielding his iconic thunderbolt.
Planetary Naming Context
How Planets Are Named Today
Naming a new planet involves several deliberate steps, starting with its discovery by astronomers who confirm the existence of a new celestial body. Suggestions for names often draw from historical significance, cultural relevance, or mythological connections, such as the powerful god Jupiter, known for his role in the Roman pantheon. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) plays a critical role in this process, ensuring that names are unique and suitable for the astronomical community while considering public input and cultural factors.
Role of Mythology in Naming
Mythology is a huge part of planetary naming tradition. It links our human stories and struggles with the great and abiding mysteries of the cosmos. Planets such as Jupiter, after the Roman god who ruled over other gods, keep these stories alive even today.
Mythological themes echo our exploration, mirroring human experiences and the wonder of the cosmos that we seek to capture. Mars and Venus still wear names of mythological characters. This deepens our beautiful, ancient bond between tales and the cosmos.
This legacy ripples down to today, shaping both the way we view and the way we name new discoveries. The mythological legacy continues, offering astronomers and astronomy lovers a treasure trove of inspiration.
Conclusion
Jupiter’s name has a deep and fascinating history, with roots in mythology and culture. Named after a Roman god, famous for his tremendous strength. Its name isn’t merely an honorific, it’s a bridge linking us to yesterdays and their stories. That lasting legacy continues to inspire us to look up and explore.
So the next time you look up at the night sky, take note of the amazing history behind Jupiter’s well-earned name. As always, go out and stay interested, stay educated, and get involved in exploring the universe’s wonders.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did Jupiter get its name?
Jupiter, named after the king of the Roman gods, is considered a powerful god associated with thunder and the sky.
How does Jupiter’s name differ in other languages?
In French, it’s “Jupiter”; in Spanish, “Júpiter”; and in German, “Jupiter.” Almost all languages today follow the same pattern, using some variation of the original Latin-derived name of the powerful god from the Roman pantheon.
Why is Jupiter important in astronomy?
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun and a giant planet in our solar system, is the largest among the classical planets. Its enormous size and beautiful features, such as the Great Red Spot, make it a captivating subject for study.
What is the cultural impact of Jupiter’s name?
Jupiter, named after the powerful Roman god, has profoundly influenced art, literature, and astrology, evoking grandeur across multiple cultures.
How are planets usually named?
Planets, including the planet Jupiter, are traditionally named after mythological gods and goddesses, a practice rooted in Roman traditions and Greek mythology.
Would you like to receive similar articles by email?